What is high blood pressure?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a condition in which the force of blood flowing through a person’s blood vessels is consistently too high. Over time, this puts stress on the arteries, the heart and the kidneys, which increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.1
While diet, exercise and medications are the first-line treatments, it can still be challenging to meet the target blood pressure goal.
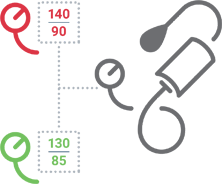
Normal blood pressure is <120/80 mmHg. A blood pressure of 130/80 mmHg is considered high blood pressure.² Depending upon your age and health status, your physician will help you identify the target blood pressure that is optimal for you.

Managing high blood pressure
Diet, exercise, and medications are the first-line treatments for hypertension. Less than half of patients treated for hypertension achieve a target BP of less than 140/90 mmHg.3
Appropriate lifestyle changes are the cornerstone for the prevention of hypertension and are also important for its treatment. If your blood pressure remains higher than 130/80 mmHg despite appropriate lifestyle changes, your physician will likely prescribe antihypertensive medications.2
A growing area of research
For patients unable to effectively control their blood pressure with lifestyle changes and medication therapy, a new class of interventional products are under clinical investigation for the treatment of hypertension using a procedure called renal denervation.3
This investigational procedure has the objective of ablating these sympathetic nerves in order to reduce their overactivity. The overactive sympathetic nervous system may play a role not only in hypertension, but also in heart failure, kidney disease, metabolic syndrome and sleep apnea.6, 7
1 https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov
2 Whelton et al, 2017 ACC/AHA /AAPA/ABC /ACPM/AGS/APhA/ ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults, Journal of the American College of Cardiology May 2018, 71 (19) e127-e248; DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.006
3 Williams et al, 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension, European Heart Journal (2018), 1–98 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339
4 Schmieder et al, European Society of Hypertension Position Paper on Renal Denervation 2018, Journal of Hypertension 2018 Oct;36(10):2042-2048.
5 Mahfoud et al, Proceedings from the 2nd European Consensus Conference for device-based therapies for hypertension: state of the art and considerations for the future, European Heart Journal (2018) 0,1-6 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehy584
6 Mahfoud et al, Catheter-based renal denervation in hypertension: heading for new shores, J Hypertension 2018 January; 36(1): 41-42
7 Fisher et al, Central Sympathetic Overactivity: Maladies and Mechanisms, Auton Neurosci. 2009 June 15; 148(1-2): 5–15. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2009.02.003


